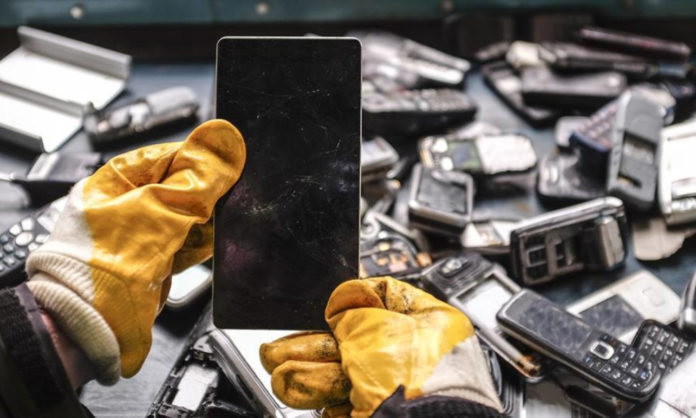
According to study, a lot of consumers keep their old phones rather than recycle them. The cobalt in rechargeable batteries and the copper in wiring are precious minerals that cannot be obtained from used devices and must be mined.
Worldwide, there are about 16 billion mobile phones; in Europe, just around a third, are still in use. The “mountain” of electrical and electronic trash, which includes everything from washing machines and toasters to tablet computers and global positioning system (GPS) gadgets, will reach 74 million tons annually by 2030, according to data by the WEEE. The Royal Society of Chemistry, earlier this year, started a campaign advocating the mining of e-waste to create new goods, emphasizing how international instability, such as the situation in Ukraine, affects supply chains for precious metals.
Importance of E-waste

Magdalena Charytanowicz of the WEEE claims that these devices offer many precious assets that can be used in the development of new electronic devices or other equipment, such as wind turbines, electric car batteries, or solar panels – all essential for the green, switchover to low-carbon societies.
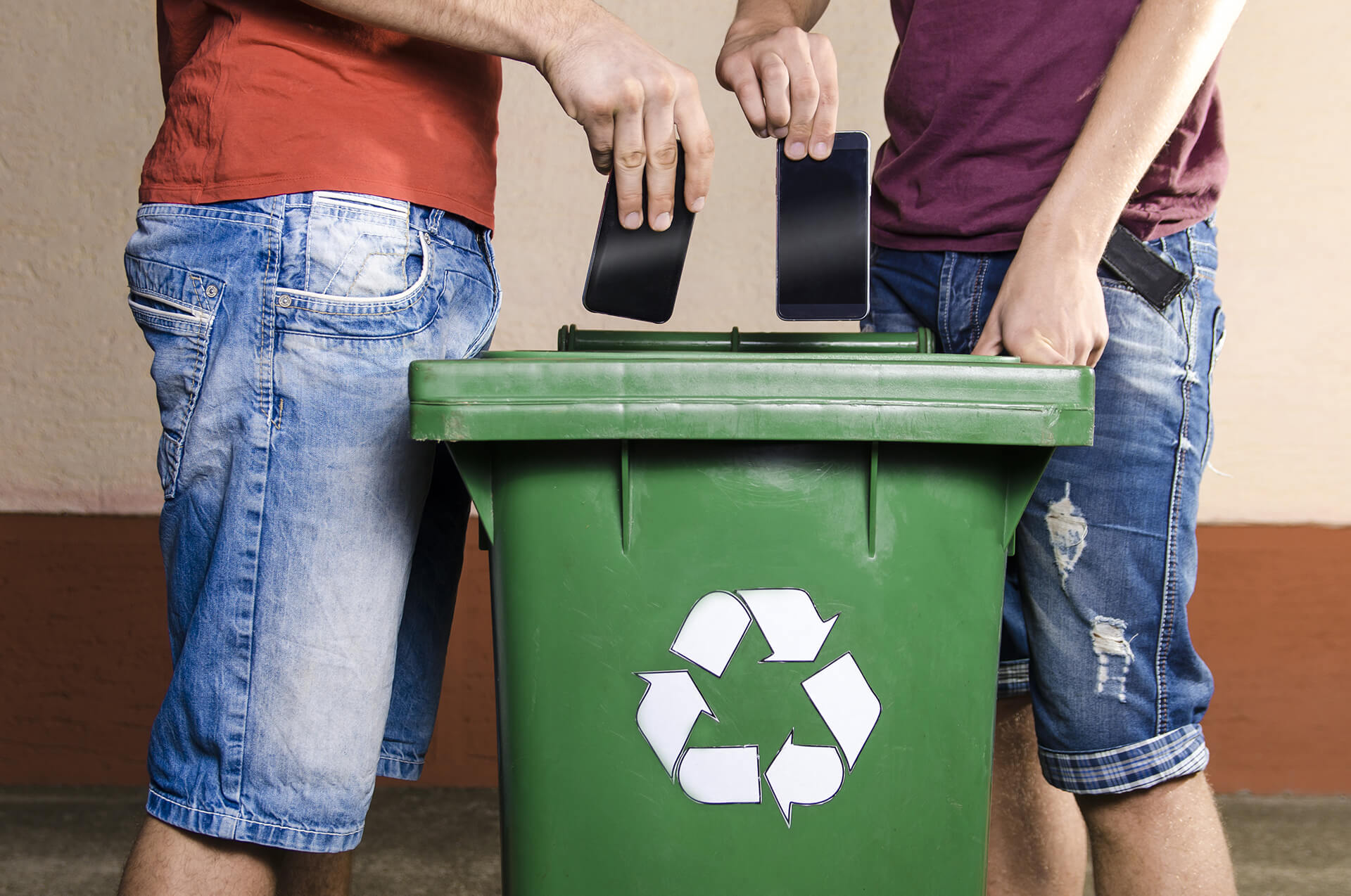
Only a little more than 17% of the world’s e-waste is now properly recycled, but the International Telecommunication Union of the United Nations has set a goal to increase that to 30% by the end of the year. It states that because it may include dangerous elements as it is one of the “fastest increasing and most complicated waste streams that harms both human health and the environment.”
According to studies by the organization Material Focus, there are presently more than 20 million functional but underused electrical equipment stockpiled in UK households, with a potential value of £5.63 billion. It also estimated that the typical UK family might make approximately £200 by selling unused technology.
The impact of Geo-political situation
According to experts, mining the Earth for precious metals to create new technology is unsustainable; hence there is an urgent need to increase e-waste recycling. It highlights how the price of commodities like nickel, a crucial component in electric car batteries, has skyrocketed as a result of global upheaval, especially the conflict in Ukraine.

Chaos in supply chains that allow the creation of electronics is being brought on by this volatility in the market for materials. This led to the price of lithium, another crucial element in battery technology, to rise by about 500% between 2021 and 2022 when combined with the jump in demand.
Stay tuned to Brandsynario for the latest news and updates.