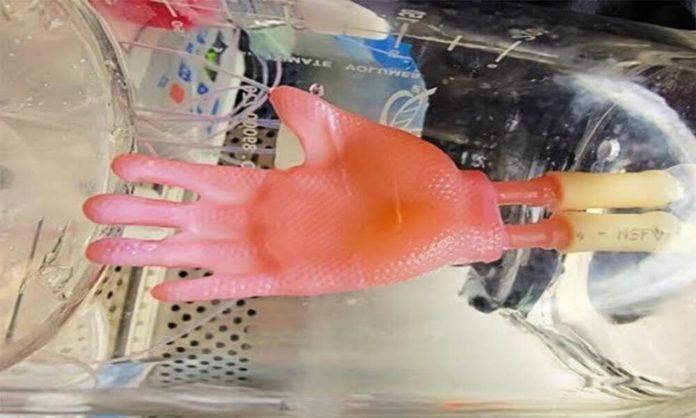
Scientists from Columbia University have devised a plan to solve the problems faced in tissue grafting. According to the latest research done by engineers, they have now found a way to grow skin in a 3D structured pattern that will allow the victims to wear the skin seamlessly like a glove.
3D Engineered Skin
The skin graft is prepared by using a 3D scan of the target structure such as a human hand. Followed by creating a series of hollow, permeable models with the help of computer-aided designs and 3D printing. The outer surface of the model is then seeded with skin fibroblasts, which generate the skin’s connective tissue, and collagen (a structural protein). Finally, the outside of the mold is coated with a mixture of keratinocytes (cells that comprise most of the outer skin layer, or epidermis) and the inside is perfused with growth media, which support and nourish the developing graft.
According to Hasan Erbil Abaci, Ph.D., assistant professor of dermatology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons. “Three-dimensional skin constructs that can be transplanted as ‘biological clothing’ would have many advantages. They would dramatically minimize the need for suturing, reduce the length of surgeries, and improve aesthetic outcomes.”
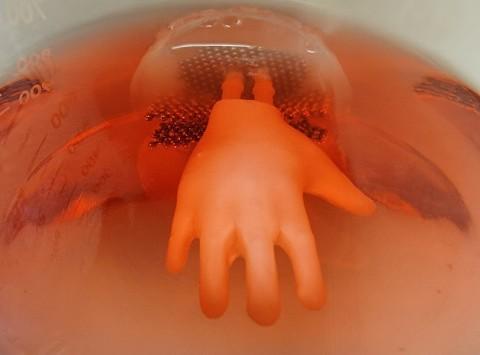
3D Hand Scaffolding
“As a bioengineer, it’s always bothered me that the skin’s geometry was overlooked and grafts have been made with open boundaries or edges. We know from bioengineering other organs that geometry is an important factor that affects function.”
Read More: Here’s How Sitting In Traffic Is Causing Brain Damage
“We hypothesized that a 3D fully enclosed shape would more closely mimic our natural skin and be stronger mechanically. That’s what we found. Simply remaining faithful to the continuous geometry of human skin significantly improves the composition, structure, and strength of the graft.” He added.
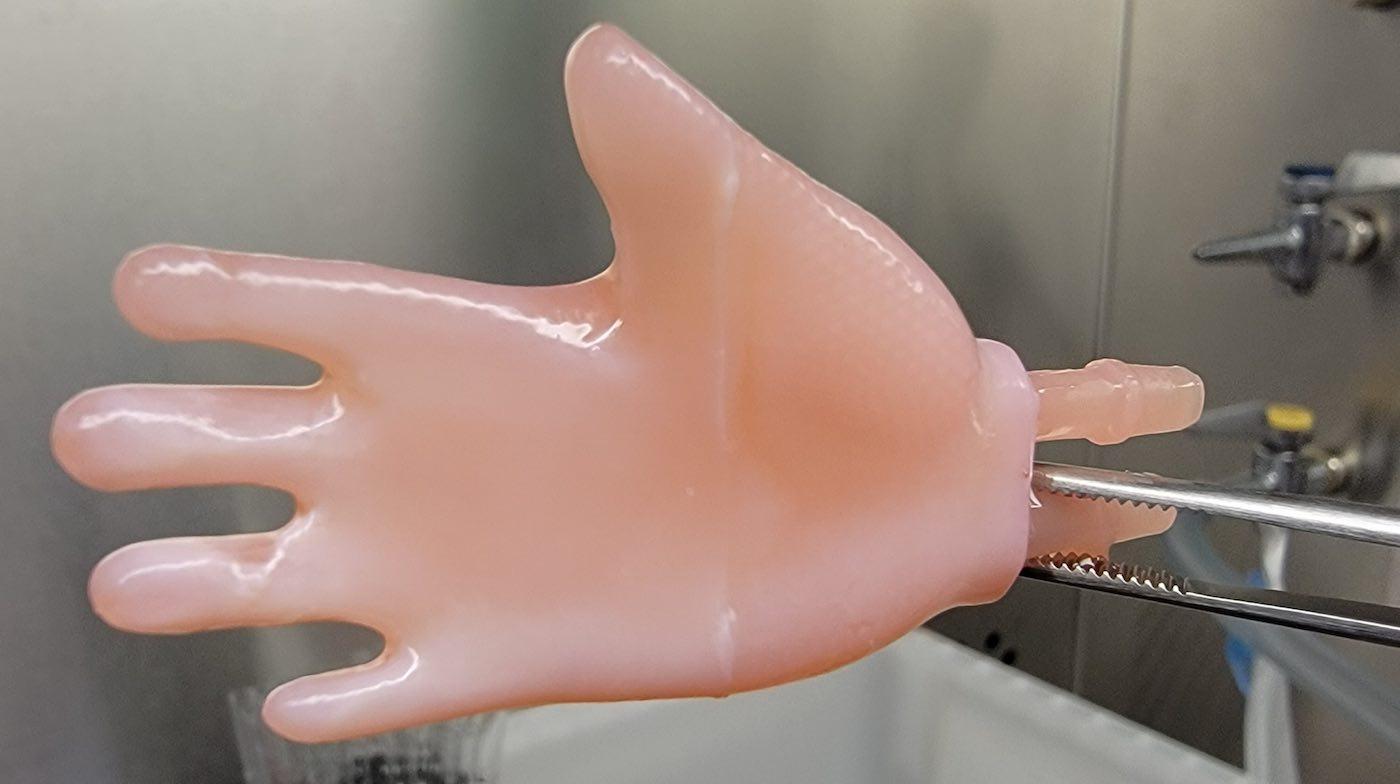
For future development, Abaci mentions the development of custom-made grafts using the patient’s cells. Such grafts can be made by using only a 4X4 mm skin sample. This will allow enough cells which can be cultured and multiplied to create enough skin to cover a human hand.
Read More: Are Cough Syrups Causing Children To Die? WHO Investigates
Stay tuned to Brandsynario for the latest news and updates.