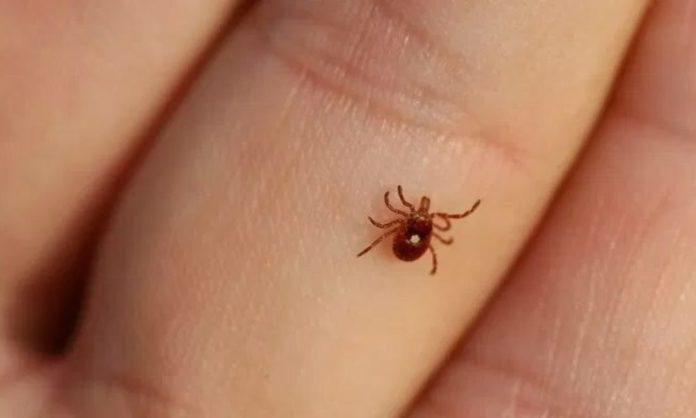
Congo virus is a highly-infectious disease that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks or contact with the blood and body fluids of infected animals, particularly livestock such as goats and cattle. With Eid-ul-Adha right around the corner, all cities of Karachi are at a high risk of Congo virus cases.
The virus is mainly prevalent in many African countries, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it was first identified in 1956. But now it might be the next global pandemic.
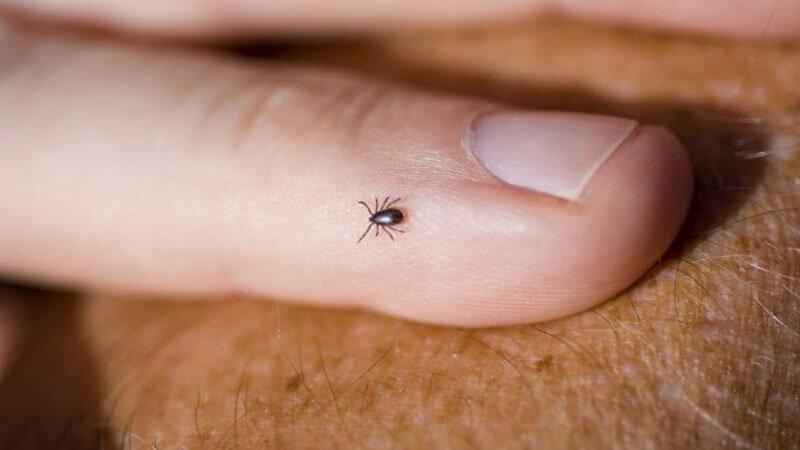

Congo Virus In Karachi
Karachi has now unfortunately discovered its first case of Congo Virus. On Monday, a man aged 28, who was identified as Mohammad Adil and worked as a meat seller in Liaquatabad, passed away while receiving treatment at a private hospital in Karachi. He was confirmed as the first case of Congo virus this year.
Similarly, this was the fourth death from the virus in the last 10 days. On May 2, a 20-year-old woman in Quetta also passed away due to the Congo virus.
How Does It Spread?
Congo virus is primarily spread through the bite of infected ticks, particularly the Hyalomma tick species. Here’s what they look like.
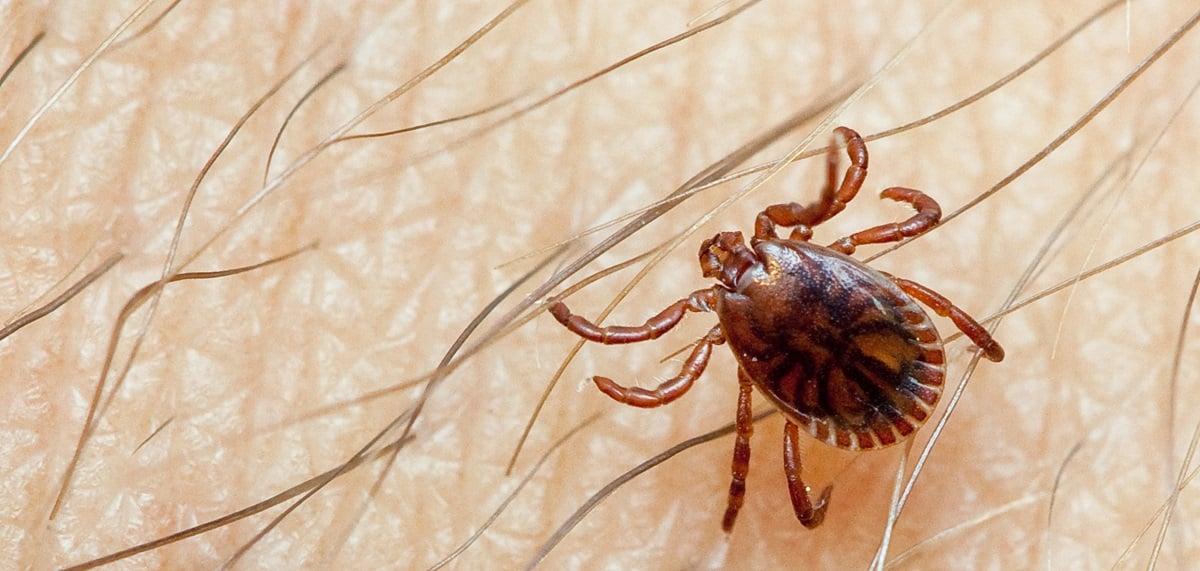
These ticks are commonly found on domesticated and wild animals, such as goats, sheep, cows, and camels. So basically, this Eid ul Adha, everyone is on high alert when taking care of their sacrificial animals. Humans can also get the virus by coming into contact with the blood, body fluids, or tissues of infected animals.
For example, people who work with animals or in slaughterhouses are at higher risk of contracting the virus. However, human-to-human transmission is rare and only occurs through close contact with infected bodily fluids.
Symptoms
The initial symptoms include;
- fever
- headache
- muscle pain
- weakness
As the disease progresses, patients may experience more severe symptoms, such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bleeding from the mouth, nose, and other organs. In some cases, patients may also develop jaundice, confusion, and seizures.
Severe cases can lead to hemorrhagic fever, which is characterized by internal bleeding and can be life-threatening. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of the Congo virus, especially if you have been exposed to ticks or infected animals.
Treatments
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment or vaccine for the Congo virus, but medical care can help manage symptoms and improve survival chances. Treatment includes hospitalization and supportive care, such as intravenous fluids, pain relievers, and blood transfusions if necessary. To prevent the
Congo virus, wear protective clothing, use tick repellents, and avoid contact with infected individuals and animals. At home, you can safely dispose of materials contaminated with blood or bodily fluids to prevent the spread of the virus.
Stay tuned to Brandsynario for more news and updates.











































